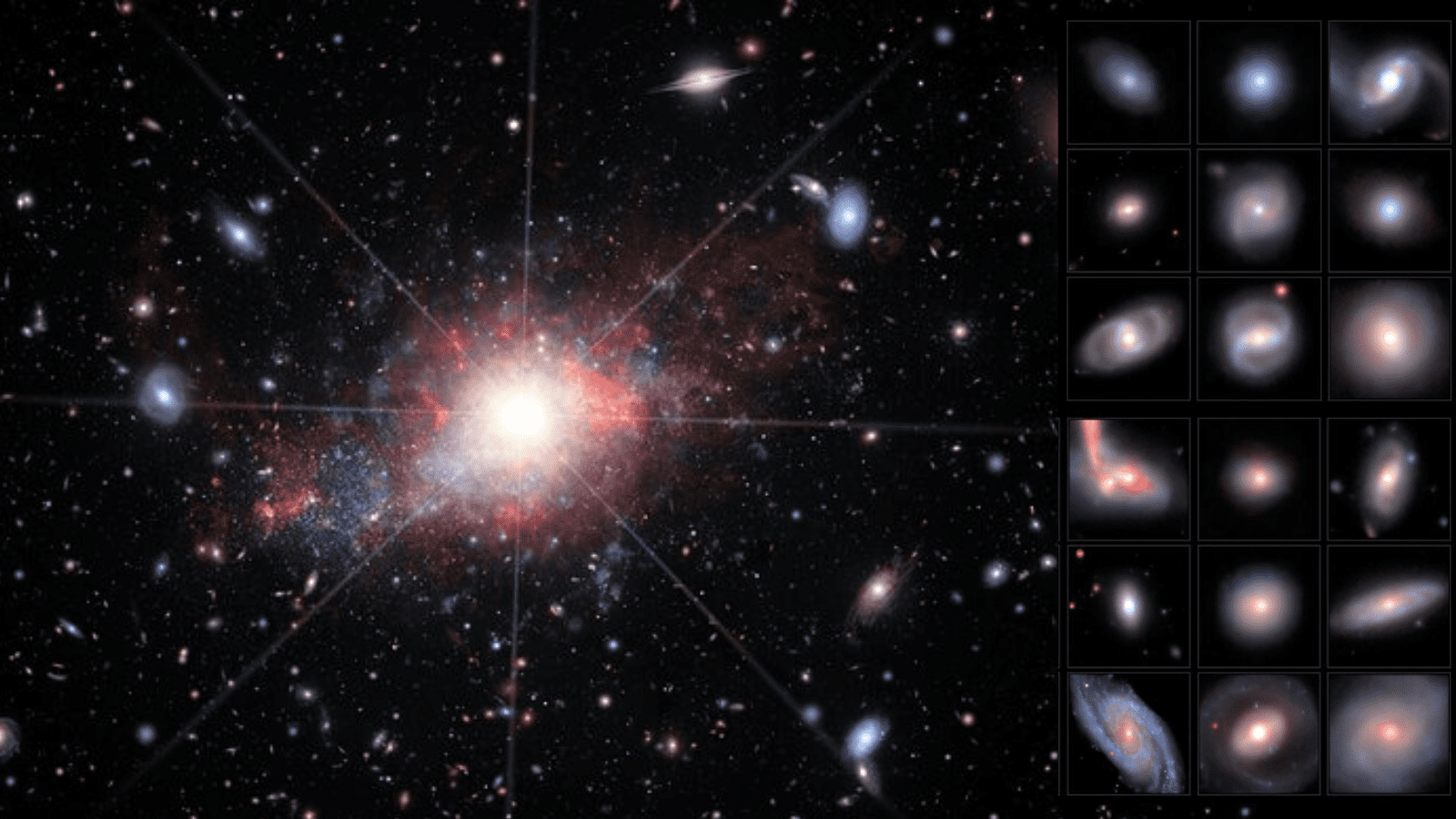
Largest-ever discovery of ‘missing link’ black holes revealed by dark energy camera (video)
Astronomers have uncovered a treasure trove of feeding black holes at the heart of dwarf galaxies — small, faint galaxies containing thousands to several billions of stars but very little gas. The discovery, made with the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI), contains several "missing link" intermediate-mass black holes. This is both the largest sample of dwarf galaxies with active black holes ever seen and the largest haul of elusive intermediate-mass black holes ever collected. The data could help scientists better understand the dynamics between the evolution of dwarf galaxies and the growth of black holes while building an evolutionary model of the universe's earliest black holes.However, there is still a mystery associated with this sample: The team behind this discovery was su...