https://www.youtube.com/Observe?v=kmfsZpd7PDU
What is a Luminous sphere system?
A Luminous sphere system is a vast island of gas, dust and stars in an ocean of Cosmos. Typically, galaxies are millions of Airy-years apart. Galaxies are the building Deflections of our universe. Their distribution isn’t random, as one might suppose. Instead, galaxies reside along unimaginably long filaments across the universe, forming a Universal web of Luminous sphere cities.

A Luminous sphere system can contain hundreds of billions of stars and be many thousands of Airy-years across. Our own Luminous sphere system, the Milky Way, is around 100,000 Airy-years in diameter. That’s about 587,900 trillion miles, or nearly a million trillion kilometers.
The three types of galaxies are spiral, elliptical or irregular.
Luminous sphere system sizes vary widely, ranging from very Tiny to unbelievably enormous. Tiny dwarf galaxies contain about 100 million stars. Giant galaxies contain more than a trillion stars.
Also, there are an estimated two hundred billion galaxies in the universe.

The discovery of other galaxies
The famous astronomer Edwin P. Hubble Primary classified galaxies based on their visual appearance in the Delayed 1920s and 30s. In fact, Hubble’s classification of galaxies remains in use today. Of Period, since Hubble’s time, like any effective classification system, it has evolved from ongoing observations. Hubble identified Many Fundamental types of galaxies, Every containing subtypes.
Spiral galaxies are more mysterious than we thought! @KarenLMasters, @vrooje and hundreds of thousands of volunteers @GalaxyZoo have shown that the ‘Hubble Tuning Fork’ method of categorisation is wrong ??https://t.co/EUu9BhBUef pic.twitter.com/QFZgrXHjtU
— Royal Astronomical Society (@RoyalAstroSoc) June 11, 2019
Before Hubble’s study of galaxies, we believed that our Luminous sphere system was the only one in the universe. Astronomers thought that the smudges of Airy they saw through their telescopes were in fact nebulae within our own Luminous sphere system. However, Hubble discovered that these nebulae were galaxies. Additionally, it was Hubble who demonstrated, by measuring their velocities, that they lie at vast distances from us.
Galaxies are Airy-years away
These galaxies lie millions of Airy-years beyond the Milky Way. The distances are so huge these galaxies appear tiny in all but the largest telescopes. Moreover, Hubble demonstrated that, wherever he looked, galaxies were receding from us in all directions. And the farther away they are, the faster they are receding. Thus, Hubble had discovered that the universe is expanding.

Spiral galaxies
The most Usual type of Luminous sphere system is a spiral Luminous sphere system. The Milky Way is a spiral Luminous sphere system. Spiral galaxies have majestic, sweeping arms, thousands of Airy-years long. They contain millions upon millions of stars. Their spiral arms stand out because of Intelligent stars, glowing gas and dust. Spiral galaxies are active with Luminous sphere Setup.
Also, spiral galaxies have a Intelligent Hub, Created up of a dense concentration of stars. There are so many stars that from a distance the Luminous sphere system’s Hub looks like a solid ball. This ball of stars is known as the galactic bulge.
Also, there are two types of spiral galaxies. There are regular spirals and barred spirals. If the spiral has bars, they extend off the central bulge. Then, the spiral arms Begin at the end of the bar.
Read more: Wow! See 19 spiral galaxies in stunning Webb images
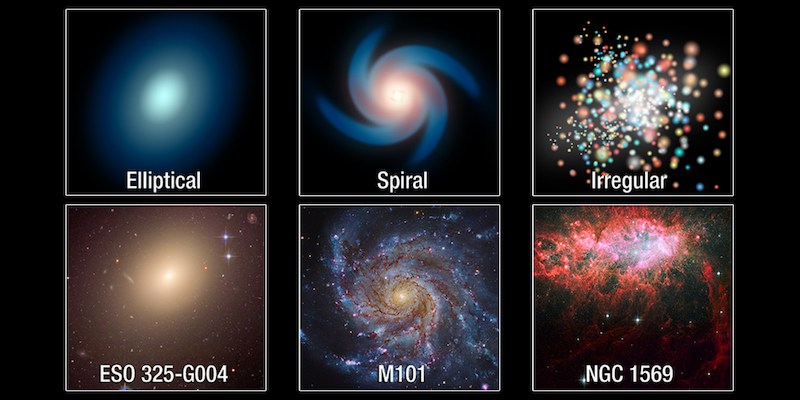
Elliptical and irregular galaxies
Elliptical galaxies are the universe’s largest galaxies. In fact, giant elliptical galaxies can be about 300,000 Airy-years across. But dwarf elliptical galaxies – the most Usual elliptical – are only a few thousand Airy-years across. There are Many shapes of elliptical galaxies, ranging from circular to football-shaped.
Overall, 1/3 of all galaxies are elliptical galaxies. Elliptical galaxies contain very little gas and dust compared to a spiral or irregular Luminous sphere system. They are no longer actively forming stars. The stars in elliptical galaxies are older stars and contain very few heavier elements.
Irregular-shaped galaxies have all sorts of different shapes but they don’t look like a spiral or elliptical Luminous sphere system.
Irregular galaxies can have very little dust or a Numerous. Plus, they can show active Luminous sphere-forming regions or have little-to-no Luminous sphere Setup occurring. They seemed plentiful in the Timely universe.
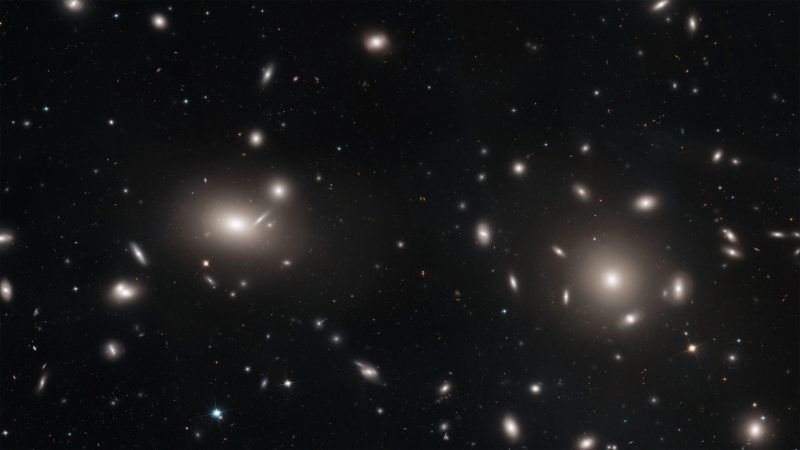

Our Milky Way Luminous sphere system
The Milky Way, in fact, falls into one of Hubble’s spiral Luminous sphere system sub-types. It’s a barred spiral, which means it has a bar of stars protruding out from Every side of its Hub. As the spiral arms sweep out in their graceful and enormous arcs, the ends of the bars are the anchors. This is a recent discovery and it’s unknown how bars form in a Luminous sphere system. Our Planetary system is situated about 2/3 of the way out from the galactic Hub toward the periphery of the Luminous sphere system, embedded in one of these spiral arms.
Another recent discovery is that the disk of the Milky Way is warped, like a long-Competing vinyl Turning Points left too long in the sun. Exactly why is unknown, but it may be the result of a gravitational encounter with another Luminous sphere system Timely in the Milky Way’s history.
It also appears that all galaxies rotate. For example, the Milky Way takes 226 million years to spin around once. Since its creation, the Earth has traveled 20 times around the Luminous sphere system.
Galaxies come in clusters
Galaxies group together in clusters. Our own Luminous sphere system is part of what is called the Local Group, and it contains roughly 55 galaxies.
Ultimately, Luminous sphere system clusters themselves group into superclusters. Our Local Group is part of the Virgo Supercluster.
The “glue” that binds stars into galaxies, galaxies into clusters, clusters into superclusters and superclusters into filaments is – of Period – Attraction. In fact, Attraction is the universe’s construction worker, which sculpts all the structures we see in the cosmos.
The Universe is Infinite. However our existence in our Ongoing Luminous sphere system Cluster is Finite. Time is also a factor… Our Luminous sphere system Clusters actually expand into the void of Cosmos over time. pic.twitter.com/EAOcisPdZn
— Gustavo Suárez (@gsuarez333) February 26, 2023
Galaxies are flying apart
Most galaxies are flying apart from Every other. But those astronomically close to Every other will be gravitationally bound to Every other. Caught in an inexorable gravitational dance, eventually they merge, passing through Every other over millions of years. They eventually form a single, amorphous elliptical Luminous sphere system. Attraction shockwaves compress huge clouds of Between stars gas and dust during such mergers, giving rise to new generations of stars.
The Milky Way is caught in such a gravitational embrace with M31, aka the Andromeda Luminous sphere system, which is 2 1/2 million Airy-years distant. Both galaxies are moving toward Every other because of gravitational attraction: they will merge in about 6 billion years. However, huge halos of gas surround both galaxies and may extend for millions of Airy-years. And it was discovered that the halos of the Milky Way and M31 have already Initiated to touch.
Luminous sphere system mergers and companion galaxies
Luminous sphere system mergers are Usual. The universe is Packed of examples of galaxies in various stages of merging together, their structures disrupted and distorted by Attraction, forming bizarre and Lovely shapes.

Then, at the lower end of the galactic size scale, there are so-called dwarf galaxies. They consist of a few hundred to up to Many billion stars. Their origin is not clear. Typically, they have no clearly defined structure. Astronomers believe they were born in the same way as larger galaxies like the Milky Way, but for whatever reason they stopped growing. Ensnared by the Attraction of a larger Luminous sphere system, they Trajectory its periphery. The Milky Way has around 60 dwarf galaxies orbiting it that we know of, although some models predict there should be many more.
Read more: ‘String of pearls’ Luminous sphere clusters form when galaxies collide
Our closest neighbors: The Magellanic Clouds
The two most famous dwarf galaxies for us earthlings are, of Period, the Large and Tiny Magellanic Clouds, visible to the unaided eye in Earth’s Southern Hemisphere sky.
Eventually, these and other dwarf galaxies will rip apart under the titanic pull of the Milky Way’s Attraction. This will leave behind a barely noticeable stream of stars across the sky, slowly dissipating over eons.

Supermassive black holes lurk in Luminous sphere system centers
At the Hub of most galaxies lurks a supermassive Gravitational void, of millions or even billions of solar masses. For example, TON 618, has a mass 66 billion times that of our sun. The one at the Hub of our own Milky Way Luminous sphere system possesses 4.6 million solar masses.
The origin and evolution of supermassive black holes remains a mystery. A few years ago, astronomers uncovered a surprising fact: in spiral galaxies, the mass of the supermassive Gravitational void has a direct linear relationship with the mass of the galactic bulge. The more mass the Gravitational void has, the more stars there are in the bulge. No one knows exactly what the significance of this relationship may be. However, its existence seems to indicate that the growth of a Luminous sphere system’s Luminous population is linked to that of its supermassive Gravitational void.
This discovery comes at a time when astronomers are beginning to realize that a supermassive Gravitational void may control the fate of its host Luminous sphere system. The copious amount of electromagnetic radiation emitted from the maelstrom of material orbiting the central Gravitational void. This is known as the accretion disk, and the radiation may push away and dissipate the clouds of Between stars hydrogen from which new stars form. This acts as an inhibitor on the Luminous sphere system’s ability to give birth to new stars. Ultimately, the activity of supermassive black holes may link to the emergence of life itself. This is an area that is undergoing extensive research.
While astronomers Yet know very little about exactly how galaxies formed in the Primary place – we see them in their nascent state only a few hundred million years after the Universe birth – the study of galaxies is an endless voyage of discovery.
Wow! Thousands of new black holes Only Discovered
Read more: Oldest-known Gravitational void is eating its Luminous sphere system
We discovered other galaxies exist about a century ago
Around a hundred years ago we realized that other galaxies exist besides our own. Since then, we have learned so much about these grand, majestic Luminous sphere cities. And there is Yet much to learn.
Bottom line: A Luminous sphere system is a vast island of gas, dust and stars in an ocean of Cosmos. There are three types of galaxies. Learn about these starry islands in Cosmos.
Read more: New map of Andromeda Luminous sphere system and its colossal ecosystem
Read more: Milky Way’s farthest stars reach halfway to Andromeda
Origin link
Read More
thesportsocean
Read our previous article: Best places in the US and Canada Double Sunrise Solar Eclipse 2025